Yogurt is a satisfying snacking option that is high in protein and calcium to aid your daily nutritional requirements. Technically, yogurt doesn’t contain much fiber. But topping it up with some cereals or fruits helps meet your daily fiber intake.
As per FDA, For labeling purposes, the dietary fiber in yogurt can be calculated using two different methods. Yogurt manufacturers may choose either way A or method B to calculate the amount (in grams) of total dietary fiber in a serving of yogurt.
Related Posts:
- How much Yogurt is Too Much?
- What is the healthiest Dairy?
- Is it Healthy to eat Flavoured Yogurt Daily for Breakfast?
- What are the differences in Nutrition between Yogurt and Milk?
- What are the health benefits of Yogurt?
- How many Calories in a Yogurt Parfait?
- How many Carbs in Frozen Yogurt?
- How many Ounces of Yogurt in Cup?
Method A: Determine Total Dietary Fiber as Listed on the Nutrition Facts Label
The amount of total dietary fiber in a yogurt product is the difference between the weight before and after fermentation.
Protein, ash, moisture, and carbohydrate were determined for each sample type as described below. The value for dietary fiber was calculated as:
dietary fiber = [protein + (ash x 2.5) + moisture – carbohydrate] – 4.5
where dietary fiber is expressed as a percent of the total weight of the food.
Method B: Calculate Fibersol-2®, Inulin, Oligofructose, and Polydextrose Intake Using AIN-93G Criteria
In this method, manufacturers may choose to use an independent laboratory to analyze for dietary fiber using AOAC method 985.29 (Sanka, M. et al., “Determination of Total Dietary Fiber in Foods by Adsorption Analysis” J Assoc Off Anal Chem 74(5): 1244-1255 1993).
What is the FDA’s position about including “added” Dietary fiber in a Yogurt Label?
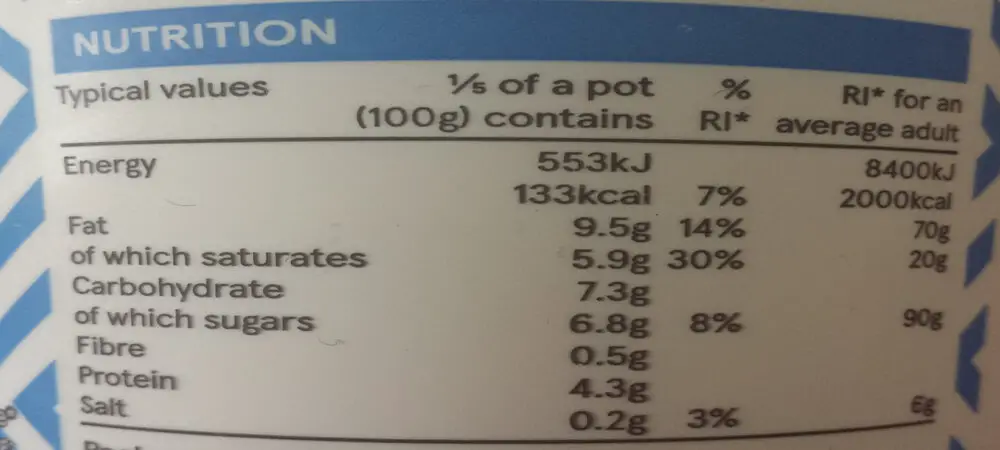
For a food to be labeled as a high, good, or excellent source of fiber, it must meet specific criteria. The criteria include having 20 percent or more of the Daily Value (DV) per reference amount customarily consumed (RACC).
Is Yogurt Good for Fiber?
Yogurt is high in calcium, protein, and phosphorus. It is also a good source of protein, vitamin B12, riboflavin, and magnesium. Yogurt contains active bacteria that are beneficial for gastrointestinal health—as with most foods, eating yogurt in moderation can be part of a healthy lifestyle. Toppin it up with 1/2 cup of cereal adds 14g of fiber to your diet.
|
Most yogurts contain 0 to 1 gram of fiber on average. The primary ingredient for any yogurt is milk which has no fiber value. However, the add-ons like fruit, nuts and coconut add to its fibrous count. |
Which Yogurt is High in Fiber?
Organic yogurt with live bacteria is the best source of fiber. Non-organic yogurts use artificial flavoring and coloring, which decreases the nutritional value. The best way to ensure you are eating a healthy yogurt is to read the label carefully and check for ingredients such as preservatives, added sugars, or artificial sweeteners.
What Happens if You Eat Yogurt Every Day?
There are many positive health benefits to eating yogurt regularly. Yogurt is made from cow’s milk, which contains lactose (a natural sugar), live cultures, and active enzymes. Consuming dairy products helps to keep your digestive system healthy. Studies show that the bacteria in yogurt might even help you absorb other nutrients like calcium better because they produce an acid that helps break down the nutrients.










