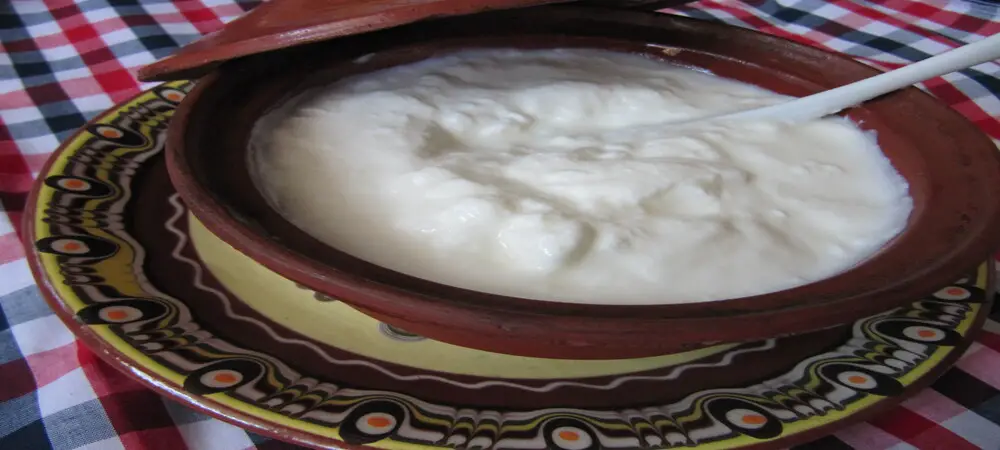
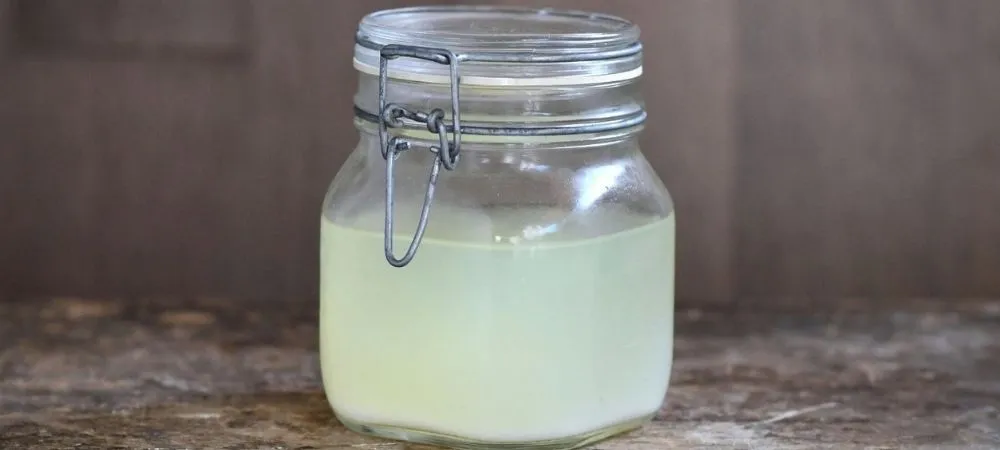
Bulgarian yogurt is known throughout the world for its richness, thickness, and high quality. It contains beneficial microorganisms which are nourishing to the intestinal flora. The unique way of preparation – Yogurt makers or Yogurt pots (Trahana) allow keeping all the tastes to themselves.
Coming to its texture and flavor, it is sourer than the other yogurts and has more jelly-like consistency. Aalso known as probiotic yogurt, this yogurt is specifically made from only two strains – Bifidus and Acidophilus. While Greek yogurt is a strained yogurt that offers a firmer texture and creaminess. But Bulgarian yogurt is an unstrained yogurt that is made from Goat, Sheep, or Buffalo milk to attain different thicknesses.
Delicious Bulgarian yogurt can be eaten plain, with honey, as a base for salad dressings and sauces. It can be added to cereals and desserts and used to prepare traditional and modern drinks and cocktails.
Yogurt is one of those rare foods with no side effects on health besides its nutritional benefits. It helps digestion by strengthening the stomach’s natural acidophilus barriers, which aid the body’s calcium absorption. It supplies a rich source of protein and vitamins B1, B2, and B6.
If you are new to this, do not hesitate in trying Organic Non Fat Bulgarian yogurts.
How is Bulgarian Yogurt Made?
It is usually considered more than 5,000 years old, and it has been known for its beneficial effects on health since ancient times. Elie Metchnikoff – Nobel Prize winner in Medicine (1908) – said that Bulgarians owed their longevity to the large amounts of yogurt they consumed daily. A recent medical study in Europe showed that Bulgarian yogurt could reduce blood cholesterol levels, normalize digestion and eliminate toxins from the body.
Bulgarian yogurt is made from pasteurized goat or sheep milk using a starter culture containing lactobacillus bulgaricus and streptococcus thermophilus. The mixture is then incubated at a temperature of 86°F (30°C) for five to eight hours. The yogurt is then chilled, and when it has set solid, it is refrigerated.
What Does Bulgarian Yogurt Contain?
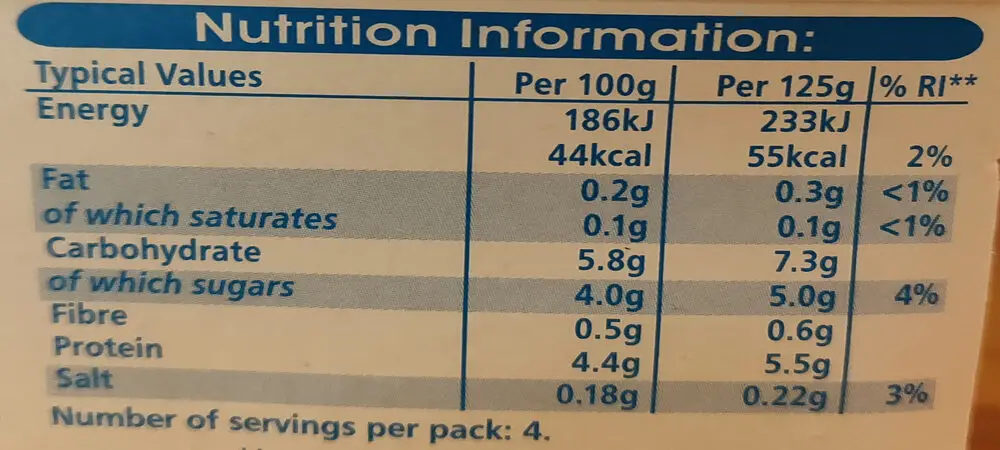
Bulgarian yogurt contains:
* approximately: 2% protein, 1% fat, 4 – 5% carbohydrate in dry matter, calcium 100-200 mg/100g.
* Bulgarian yogurt contains all essential amino acids and inappropriate quantities.
* The product has an exceptional nutritional value: the lactose and milk proteins enhance calcium absorption, and its lactic acid content contributes to systemic acid-base equilibrium.
Extensive studies show that Bulgarians who consume large amounts of locally produced yogurt have excellent health and live longer than the national average.
Yogurt is produced worldwide, but not all brands can deliver the same nutrients as Bulgarian yogurt. This product does not contain any preservatives or other chemical additives.
The “Bulgarian” label on yogurt products was made in Bulgaria by Bulgarians, and no other ingredients were added except milk and starter culture. To be considered an authentic Bulgarian yogurt, the product must have been made in Bulgaria from pasteurized milk produced from cows or sheep living in Bulgaria.
How Yogurts Are Dealt On Commercial Scale?
In countries with adequate controls over dairy production and processing, if the “yogurt” label appears on a carton, it could mean many things, depending upon the ingredients and production process. To make yogurt, milk must be inoculated with a starter culture containing live bacteria (lactobacilli), such as Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus. These organisms convert the lactose in milk to lactic acid, which gives yogurt its tart taste and thick consistency.
After the fermentation process is finished, the yogurt must be processed and packaged in clean surroundings after chilled. Finally, if any preservatives or stabilizers (such as gelatin or vegetable gums like carrageenan) are used, they must be listed on the label. Depending upon the country of origin labeling laws, yogurt made in that country or region may not have the same meaning as the term “yogurt” when used on a food label. The word yogurt does not mean anything specific in these regulations.
In Bulgaria, several hundred small dairy plants produce yogurt all through the year, but production is much higher during the summer months. Most of these small suppliers make yogurt in their small dairy plants and sell it through supermarkets, stores, and open markets.
A little bit of milk is taken from the cow or sheep, put into a container with a starter culture, and then left for several hours to ferment. The resulting yogurt is cooled down and sold very quickly because it keeps fresh only for one day.
Yogurt is one of the most widely eaten foods in the world, especially in Eastern Europe. It is a complete protein with all essential amino acids and contains many vitamins and minerals. For these reasons, it is believed that yogurt can extend life expectancy. Bulgarians are known for their long life expectancy, which has been attributed to genetics and their yogurt consumption.
Related Posts:
What’s the difference between Bulgarian Yogurt and Greek Yogurt?

They look and taste very similar, and both can be substituted for one another. The main difference is that Bulgarian yogurt has a jelly-like consistency but Greek Yogurt comes with a firmer consistency. Secondly, Greek Yogurt is a strained yogurt that is derived after the removal of whey from regular yogurt. Bulgarian yogurt is an unstained yogurt.
|
The major difference between Greek Yogurt and Bulgarian Yogurt is in their tastes. Bulgarian yogurt is sourer while the Greek Yogurt has a milder taste. |
Another considerable difference between the two is in their bacterial strains. Bulgarian yogurt is the result of two specific bacterial strains – Bifidus and Acidophilus while Greek Yogurt contains the active bacteria Bulgaricus and Thermophilius.
Is Bulgarian Yogurt better for you?
Studies have shown that Bulgarian yogurt contains higher calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, potassium, and sodium because it has not been watered down. Making Greek yogurt removes excess liquid whey, which means it is lower in these minerals. Another difference is the bacterial cultures used to make the yogurt. While both yogurts use beneficial bacteria, Bulgarian yogurt cultures contain more of them.
What are the Health Benefits of Eating Bulgarian Yogurt?
Bulgarian yogurt contains certain probiotics that may help protect your body against infections, regulate bowel movements, and reduce high cholesterol levels, according to a study by the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics. The National Yogurt Association states that all yogurts containing live and active cultures can be considered probiotic. However, not all probiotics are created equal. Bulgarians do eat a lot of yogurts, but their overall diet is very balanced and healthy.










